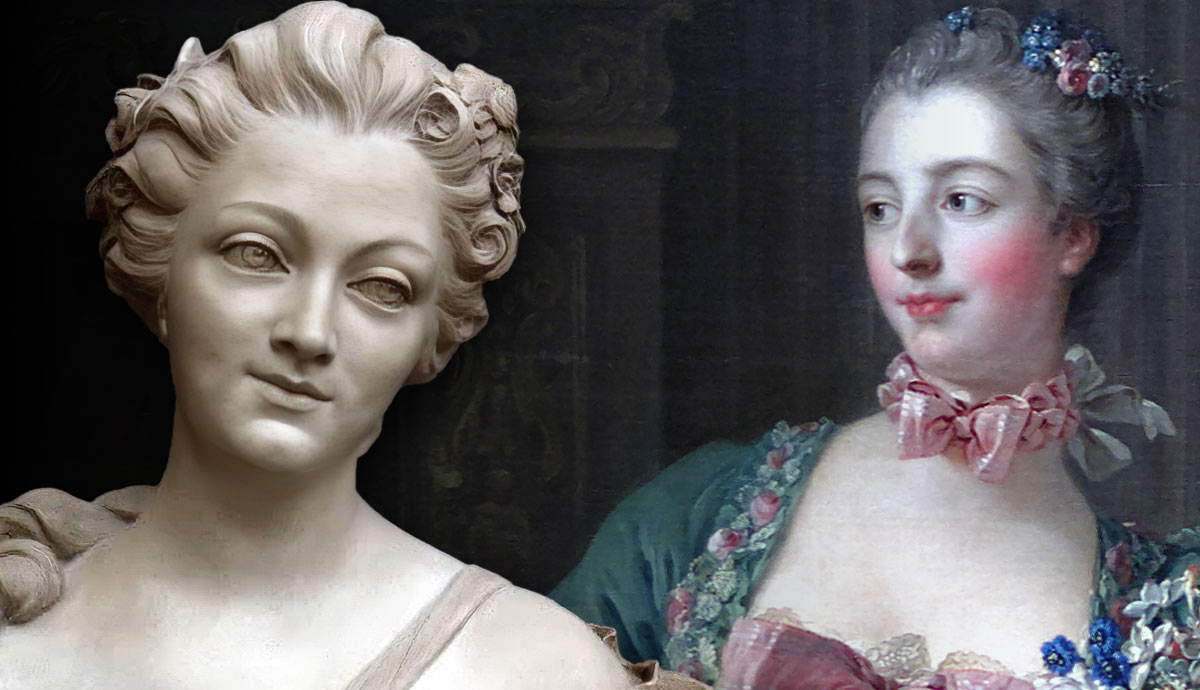
The Queen of Sheba’s visit to the court of King Solomon is described in a short and arguably uneventful biblical tale. And yet, this simple narrative has inspired a myriad of legends, stories, and artwork that explore the queen as a wealthy and wise monarch, a black Ethiopian queen, a nationalist hero, and even a half-demon and heathen with hairy legs. In this article, we will explore the origins of her fertile mythologies and learn about how different cultures, religions, and time periods have treated her legacy.
Wealth, Wisdom, and Trade: Queen of Sheba and King Solomon

The earliest mention of the Queen of Sheba can be found in the Hebrew Bible (1 Kings 10). The queen hears rumors of King Solomon’s boundless wisdom and close relationship to God. Intrigued, she travels to Jerusalem to meet and test him and brings along caravans with gold, precious stones, and camels carrying spices. When Solomon meets her in a display of riches and solves each of her riddles with ease, the queen is overwhelmed and recognizes Solomon as a valued instrument of God. She offers him gifts, and Solomon, in turn, offers her anything she desires before she returns home. A further mention is made in the New Testament (Luke 11:31), where she is described as a queen from the south who came from the ends of the earth to listen to Solomon’s wisdom.

While the story underlines Solomon’s authority and status as a prophet, it also shows the rare biblical woman with a voice of her own. We observe Solomon through the queen’s eyes and follow her as she embarks on her journey to test the famous king and presents her own wisdom and riches. As a fellow monarch worthy of testing Solomon, she is commonly depicted at the moment of arrival offering her goods, or in conversation as she poses the king riddles. From the Renaissance period, romantic or even sexualized elements occasionally creep into the story, but there is no hint of romance or sexuality yet. Instead, international trade, wisdom, and wealth are explored in the context of a meeting between two monarchs.

The historical Queen of Sheba is disputed by historians and no indication of her existence is found thus far. However, the clear reference to international trade in the biblical story does suggest a historical framework that has yielded some evidence. André Lemaire, professor of Hebrew and Aramaic Philology and Epigraphy at the Sorbonne in Paris, has uncovered an inscription that shows international trade between Judah and southern Arabia, where many historians agree the Kingdom of Sheba (or Saba) would have been located.
Conversion, Marriage, and Hairy Legs: Jewish and Islamic Storytelling

The Jewish and Islamic traditions offer a more descriptive and, in some parts, even fantastical addition to the Queen of Sheba’s account. In its skeletal form, the Qurʾān (Q. 27:15-44) describes her as a powerful queen and sun-worshipper. Solomon hears about her through the testament of a hoopoe bird, who is sent to summon her to Jerusalem to submit herself to Allah.
The queen initially responds by sending over an envoy with a gift, which Solomon immediately rejects due to his wealth being greater than any other. When the queen appears before Solomon, it is she who is tested. The palace and throne are bathed in illusion, and she believes a clear floor of crystal to be water. As she lifts her skirt and bears her claves to step into it, the queen understands she has been deceived by an illusion and subsequently converts to Islam.

The earliest Jewish post-biblical account is one Romano-Jewish historian Flavius Josephus (Antiquities 8:165-9) who reframes the Queen of Sheba’s story for a Greek and Roman audience. He speaks of a philosopher Queen of Ethiopia and Egypt who, much like in the Hebrew Bible, travels to meet Solomon to subject him to a trial of wisdom. Josephus’ legend wasn’t picked up further in medieval Jewish and Islamic legends but had a great influence on the further development of Christian tradition.
While it isn’t always clear whether the Muslim and Jewish mythologies came first, they both join in a conversation built on the same biblical past. The most prevalent story is that of Bilqīs, a sun worshiper who rules on her own with no issue. Some traditions state that her father is the king of Yemen, and her mother is a Jinn, making her a half-demon. As she walks along the palace of glass, she reveals her hairy legs which some accounts attribute to her demonic half. Solomon orders her legs to be shaven and, in certain traditions, he also marries her. The richness and details of the stories vary from text to text, but the underlying theme shows Solomon as the prophet who brings the polytheist sun worshiper to the monotheist faith.

Both religions present a woman of a certain wildness to be put before King Solomon. Her hairy legs, refusal to marry or bear children, and even the fact that she was a woman taking on a most masculine job (ruling), present her as atypical. Jacob Lassner, professor, writer, and academic in Jewish Studies, framed the Queen of Sheba’s demonic representation in the Judaic and Islamic interpretation of gender and culture. The hairiness of the queen’s legs attributes her to a masculine trait, Lassner argues, which amplifies her role as a usurper. Lassner goes as far as interpreting the act of shaving the queen’s legs, as a form of castration of the phallic woman. While some scholars feel the castration analogy goes a bit far, most agree that subjugation and conversion have replaced the astute and curious biblical queen.
I Am Black and Beautiful: The Birth of a Black Queen

Around 260 AD, early Christian scholar Origen of Alexandria wrote a commentary on the Song of Songs, a Hebrew collection of poetry that explores sexual love within marriage. Origen connects the ‘beloved’, who describes herself as “Black and Beautiful” (Song of Songs, 1:5-7), with the Queen of Sheba. He argues that in the Song of Songs, the queen represents a Gentile Church that unifies with King Solomon. Origen’s allegorical interpretation of the queen is our earliest example of her as a black woman, although her Ethiopian origins were first referenced by the aforementioned historian Flavius Josephus. The queen’s origin and skin color are of particular importance to Origen, for whom she represents the peaceful inclusion of non-Jewish religions in Christ. This has inspired some unique imagery in the early Middle Ages of the queen being represented as a regal, Black monarch.

Even though the biblical texts and medieval embellishments make no mention of the Queen’s skin color, Origen’s mystical commentary combined with Josephus’ reference to her native Ethiopia, has clearly sparked our imagination. For many of us today, the Queen of Sheba is still a notable black figure. In this context, European art has often been found guilty of whitewashing. In January of 2020, the BBC released a video where playwrights Jess Kaliisa and Jess Hagan are confronted with a painting of a white Queen of Sheba. The witty black queen was the role model who had inspired their award-winning play that explores the concept of misogynoir and the empowerment of black women.

Presenting mythical or legendary characters from diverse cultural backgrounds as Caucasian is not uncommon in western art. Andromeda, a Greek mythological figure who is the daughter of Ethiopian king Cepheus, is also commonly portrayed as a white woman. Renaissance art saw a rebirth of antiquity and mythology. Andromeda, who is described as a dark-skinned woman in Ovid’s Metamorphoses, is not usually depicted as such.
Debates did exist at the time, and Spanish Francisco Pacheco posed the question of Andromeda’s ethnicity in his Arte de la Pintura. She is so often painted as having white skin, Pachero states, while many sources describe her as black. In the few cases that she is pictured as black, examples such as Abraham van Diepenbeeck’s Andromeda show a black Andromeda with the distinct features of a white female.

In her work, Reimagining Hagar, Biblical scholar Nyasha Junior asserts that certain use of skin color is not necessarily a testament to racial thought and that these representations are subject to cultural shifts. Artistic fancies may vary, available models may lack cultural diversity, or our inability to identify with important characters who don’t share our features could influence artistic choices.
However, by the Renaissance period, around the time that the queen’s image started to transform drastically, blackness did carry a significant stigma in art. In the 15th and 16th centuries, Europe’s ties with Africa were renewed after centuries of sporadic exposure. And while intriguing representations of black figures, especially men do crop up in the context of servants, saints, and even nobility, women tend to be treated differently. Often shown as a servant to a powerful, white female, black female servants are commonly identified as “the others” whose exoticism offset the white woman’s purity and beguiling presence.

This idea of black skin color as a social marker finds its way into some famous masterpieces such as Titian’s Diana and Actaeon. Diana and her white female entourage are bathing in light. Her black servant is awkwardly positioned behind her, barely fits into the frame, and almost disappears into the background. The Queen of Sheba’s significant role in exchanging wisdom and recognizing Solomon as a prophet could have granted her an importance that separated her from the notion of otherness, although this will find some nuance in later time periods.

As diversity grew in European cities, slowly but surely, so did the complexity of the artwork. From the 17th century, we see the Queen of Sheba and the depiction of black characters started to change as a bend towards realism gained traction in Europe. Artists such as Peter Paul Rubens and Jan Boeckhorst, show a strong black queen with realistic features presenting herself and her gifts before Solomon.
Makeda of Ethiopia: A Philosopher In Her Own Right

The richest and most expansive account of the Sheba-Solomon cycle is found in the 14th-century Ethiopian epic known as the Kebra Nagast. Written by Is’haq Neburä -Id of Axum, the epic tale of the origins of Ethiopia introduces the Queen of Sheba, here known as Makeda, and her son by Solomon in no less than 74 chapters. Makeda is a philosopher queen who travels to meet Solomon in pursuit of wisdom. Contrary to the biblical account, the queen doesn’t subject Solomon to a test of riddles. Instead, the two engage in a deep, philosophical debate after which Makeda is convinced to follow the Lord God of Israel.
The Kebra Nagast introduces a romantic element to the story which is carefully sculpted around the existing Christian tradition. Solomon propositions Makeda who, as a chaste woman, resists his advances. She gets tricked into sleeping with him but, much like the Virgin Mary, remains intact. Makeda gives birth to a son, Menelik, who is described as being the spitting image of Solomon, albeit black. Menelik becomes Solomon’s heir and subtly echoes King David. Menelik’s authority is further solidified as he brings the Ark of the Covenant to Ethiopia.

In the 20th century Ethiopia, the Queen of Sheba experienced a commercial rebirth in art. By the 1940s, Ethiopian art was sold in Adis Ababa’s Mercato, but also in galleries and souvenir shops. After the Italian conquest of Ethiopia (1936-1941), tourism and expatriates caused the demand for Ethiopian art to skyrocket. Artists and even passionate hobbyists take advantage of the rising market by manufacturing artworks following an assembly line production process. The often-stereotypical reproductions include countless depictions of the legend Sheba and Solomon who had become something of a national icon in Ethiopia.
The Fertile Legends of the Queen of Sheba

A single biblical fragment has never inspired such rich iconography and legends. As a foreign monarch in awe of King Solomon’s wisdom and wealth, the Queen of Sheba is a perfect vehicle to underline Solomon’s status as a prophet and recognize the grace of the one true god. And yet, her cleverness and hunger for wisdom have also granted her the power as she travels to test a famous monarch and rules as a queen in her own right. From feminism, racial commentaries, demonic interpretations, tales of conversion, and national symbolism, the Queen of Sheba has yielded some of the most complex stories and imagery in history.